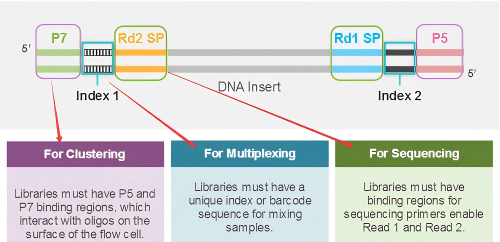
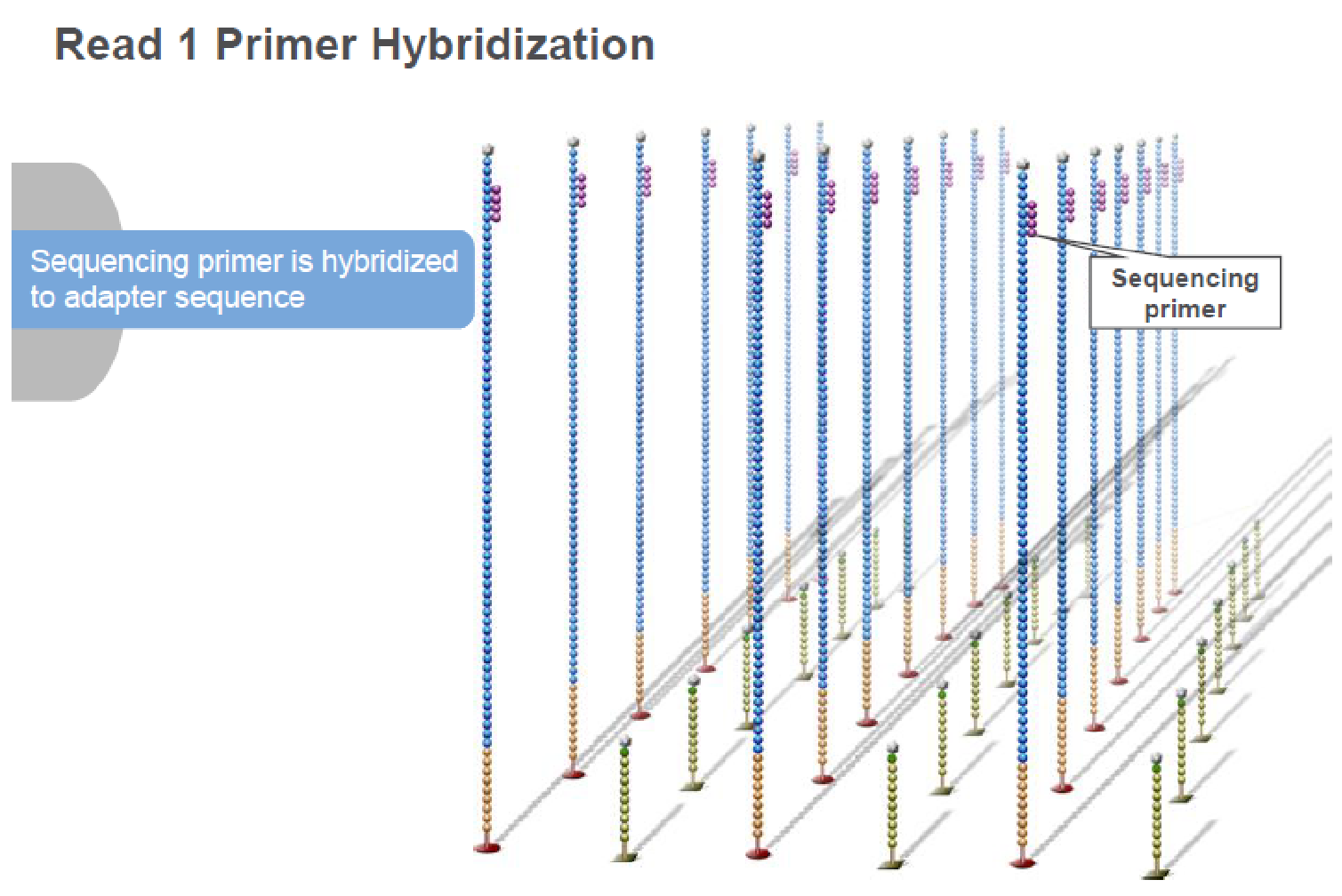
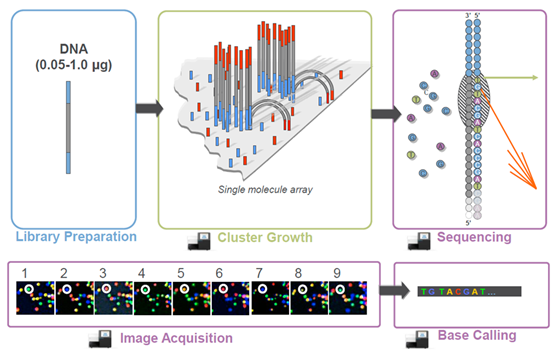
[Introduction to HLA genes]
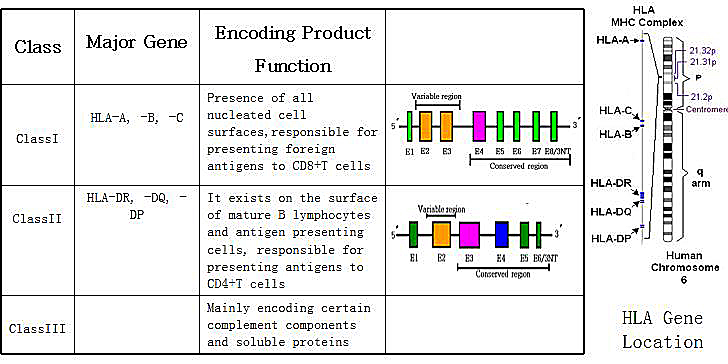
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) belongs to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and is mainly encoded by a closely linked multiple allele on the short arm of human chromosome 6. The length of this gene group is approximately 4000Kb. The main function of HLA is to mediate antigen specific recognition during the immune response, which is closely related to rejection after tissue and organ transplantation. Accurate HLA matching is of great significance to the success rate of clinical organs and bone marrow transplantation. Therefore, it is necessary to perform HLA matching between donors and recipients before transplantation. The HLA gene sequences of different people have highly complex polymorphisms and homology, making it difficult to accurately type them. [Composition of the HLA gene group]
Scientists have long been confused about the role of non-coding DNA fragments with no obvious biological function scattered in many eukaryotic protein-coding genes. These sequences, called introns, are usually spliced from their original sequences during transcription and translation and are quickly destroyed before the protein is produced. Two new studies published in the journal Nature on January 16 have unexpectedly discovered a new role for introns (at least in yeast)-many introns remain in cells for long periods of time after splicing and play an important role in regulating cell growth under stress conditions. Jurg Bhler, a geneticist at University College London who was not involved in the study, commented: "It's very surprising and exciting that things like introns, which are often considered waste, can play such a huge regulatory role under certain physiological conditions such as hunger. Since their discovery in 1977, scientists have proposed several theories about why they exist. For example, introns may play a role in regulating gene expression by delaying the time needed to convert DNA into protein. Inons also help with alternative splicing, a process that allows the ribosome to assemble multiple different proteins from a single gene.