[Introduction to dd-cfDNA]
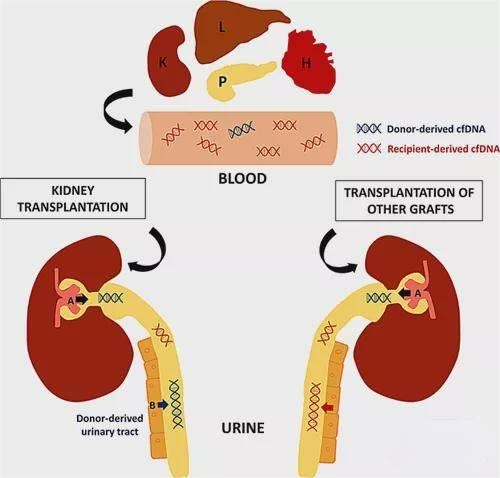
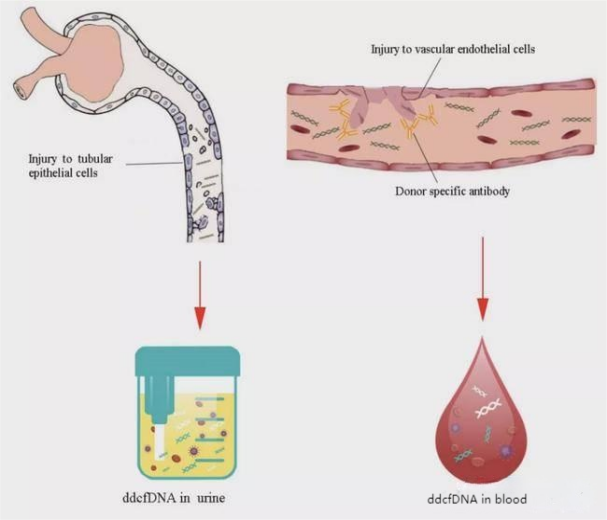
Donor-derived free DNA, or dd-cfDNA for short, refers to free DNA fragments from donor organs that exist in the recipient's blood and urine. These fragments carry information about the donor organ and can be used to assess the health of the donor organ. Status and damage sites.
[Role of dd-cfDNA in transplantation]
Organ transplantation is an effective treatment for advanced organ diseases. However, successful organ transplantation and achieving a long survival time require many "barriers", including immune tolerance and rejection barriers, infection barriers, and adaptation to new organs. Rejection and infection are common complications that affect the quality of life and life safety of transplant patients. Research by many international transplantation centers has found that dd-cfDNA technology can detect graft rejection and replace traditional needle biopsy. It has even become a routine detection method abroad.
After rejection occurs in donor organs after transplantation, the dd-cfDNA content in blood and urine increases. Based on the different content, the severity of the rejection can be assessed. Depending on the type of rejection, the amount of free DNA in blood and urine also varies, which can indicate different parts of the rejection. This technology is very sensitive, and studies have found that the concentration of free DNA has begun to rise as early as two months before the rejection occurs, allowing early rejection reactions to be detected.
[dd-cfDNA detection technology]
The dd-cfDNA detection provided by our company uses the second-generation gene sequencing platform to detect the content of donor-derived free DNA in blood or urine. It can predict the damage status of the graft and serve as a diagnostic indicator of rejection. It has the advantages of non-invasive, high sensitivity and real-time monitoring, so it is also called liquid biopsy. We extract free DNA from blood or urine, analyze low-frequency mutations with mutation frequencies less than 0.2 in SNPs, and use the maximum likelihood estimation method to conduct statistical analysis using all mutation frequencies ≤ 0.2 to obtain dd-cfDNA concentration values., which can then detect early rejection reactions.